I. Spectacular Landscapes and Rural Tourism
II. Environmental Pressures and Resource Exploitation
III. Indigenous Struggles and Historical Injustices
Main question
Documents

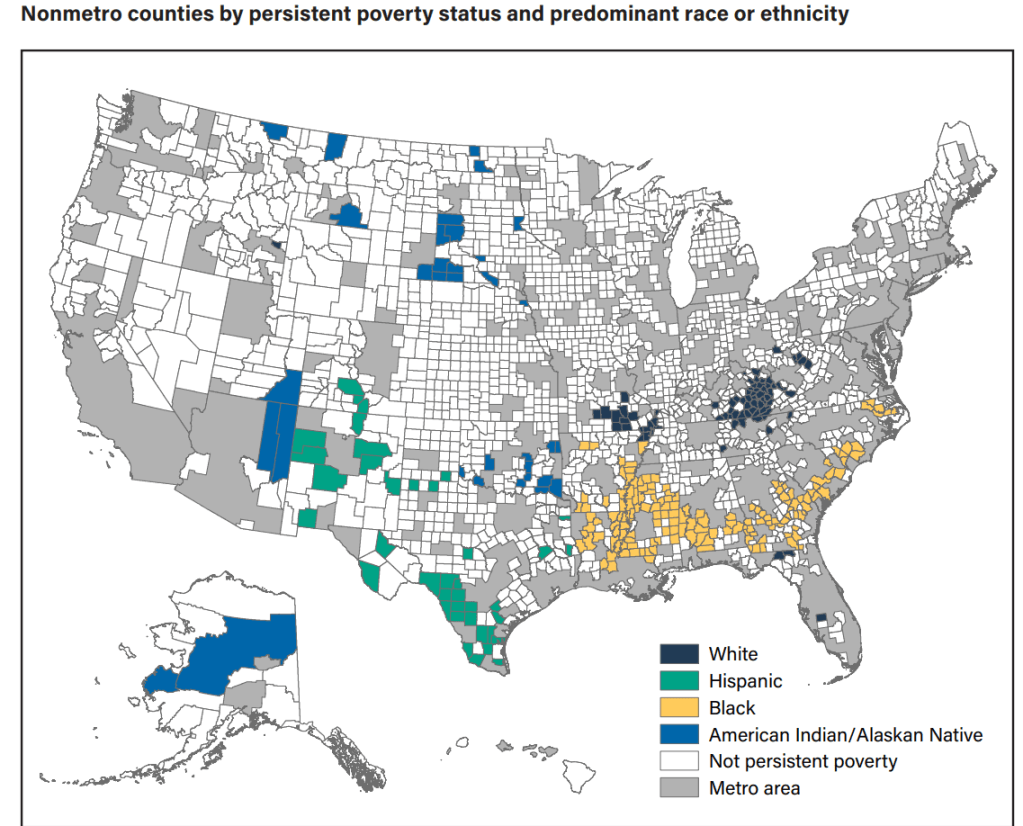

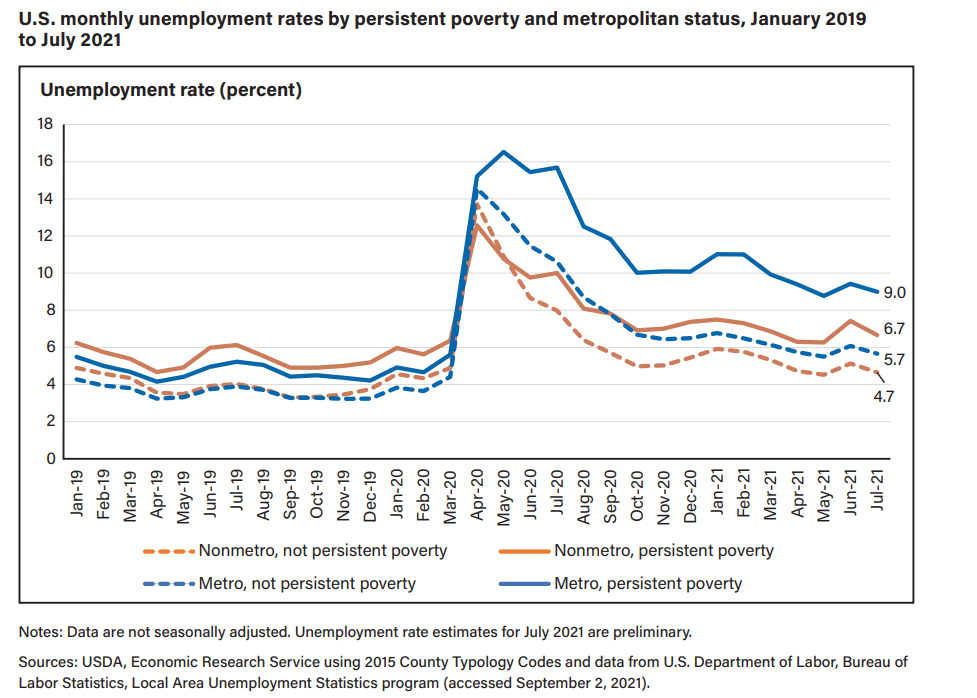
| Number of counties | Population, 2020 | Population percounty | |
| Nonmetro | 1,976 | 46,005,635 | 23,282 |
| Persistent poverty | 301 | 5,742,693 | 19,079 |
| Not persistent poverty | 1,675 | 40,262,942 | 24,038 |
| Metro | 1,166 | 285,443,646 | 244,806 |
| Persistent poverty | 52 | 11,689,533 | 224,799 |
| Not persistent poverty | 1,114 | 273,754,113 | 245,740 |
| United States | 3,142 | 331,449,281 | 105,490 |
Word box
- Rural Tourism – Visiting countryside areas for recreation, culture, and adventure.
- Spectacular Landscapes – Natural areas with impressive scenery like mountains, lakes, and forests.
- Adventure Tourism – Tourism involving physical activities like hiking, skiing, or canoeing.
- Agri-Tourism – Visiting farms to experience agriculture and rural life.
- Cottage Tourism – Staying in cottages or cabins in natural areas for relaxation.
- Sustainable Management – Practices that protect the environment while allowing tourism and development.
- Eco-Tourism – Traveling responsibly to learn about and help conserve nature.
- Deforestation – Cutting down large areas of forest, causing habitat loss.
- Resource Exploitation – Using natural resources like forests, minerals, or oil for economic gain.
- Monoculture Farming – Growing only one type of crop over large areas, which reduces biodiversity.
- Ecological Tipping Point – When environmental damage becomes irreversible, threatening ecosystems and communities.
- Indigenous Land Rights – Legal and cultural claims by Indigenous peoples to their ancestral lands.
- Environmental Resistance – Actions taken to protect land from harmful projects like pipelines or mining.
- Sovereignty – Authority of a group or nation to govern itself and protect its culture and territory.
- Historical Injustices – Past wrongs, such as unfair treaties or colonization, affecting Indigenous communities today.