I/ The Parthenon and the Panathenaic Frieze
II/ The Fate of the Frieze: From Athens to London
III/ A Cultural Dispute: Should the Frieze Be Returned?
First and second session
On a sheet of paper, choose three important figures from the frieze and describe them using the appropriate vocabulary. Then, read the arguments for or against the restitution of the frieze to Greece. Write a paragraph expressing your opinion. After the holidays, you will give an oral presentation to persuade others whether to keep the frieze in Greece or not.
Documents
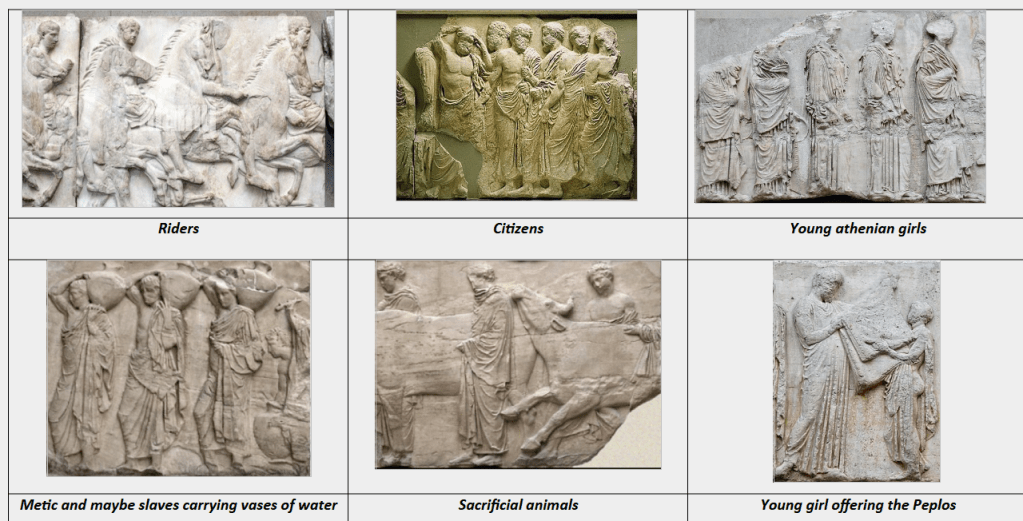


Word box
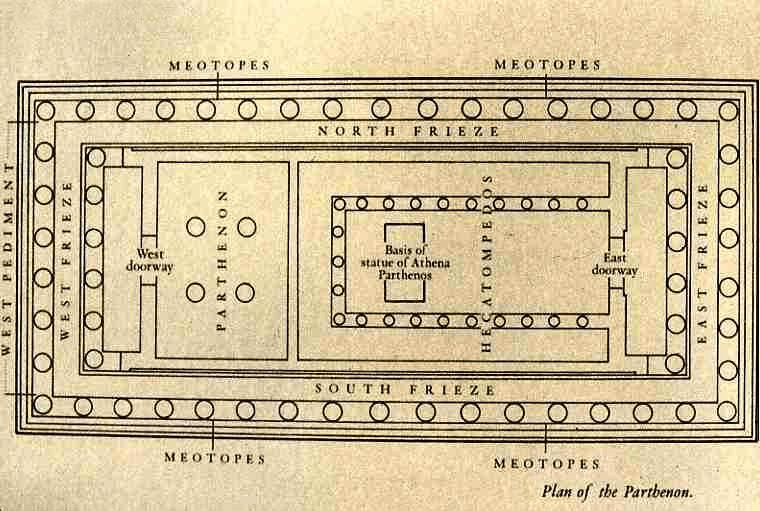
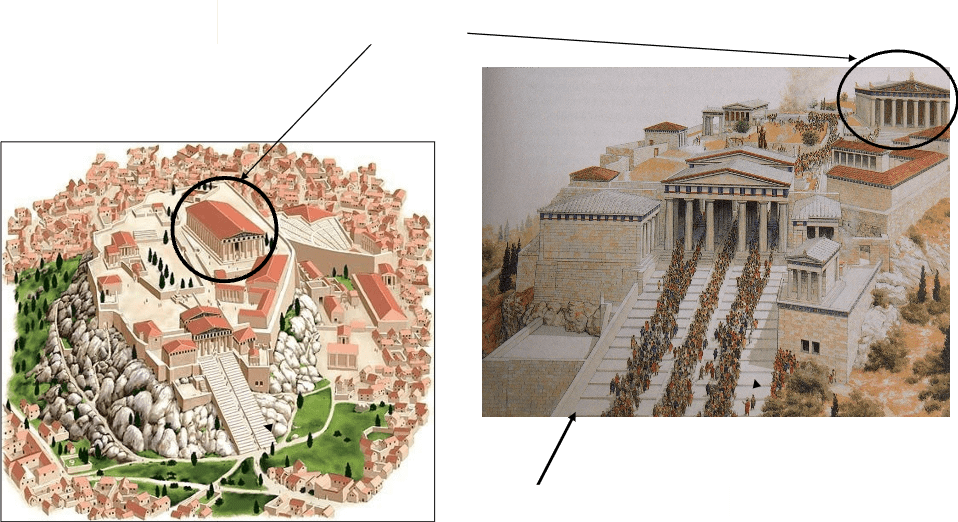
- Parthenon – A large temple on the Acropolis of Athens, dedicated to Athena, showing Classical Greek architecture.
- Acropolis – A rocky hill in Athens with important temples and buildings overlooking the city.
- Athena – Patron goddess of Athens, representing wisdom, war strategy, and protection.
- Classical Greek Architecture – Architectural style focusing on harmony, proportion, balance, and mathematical precision.
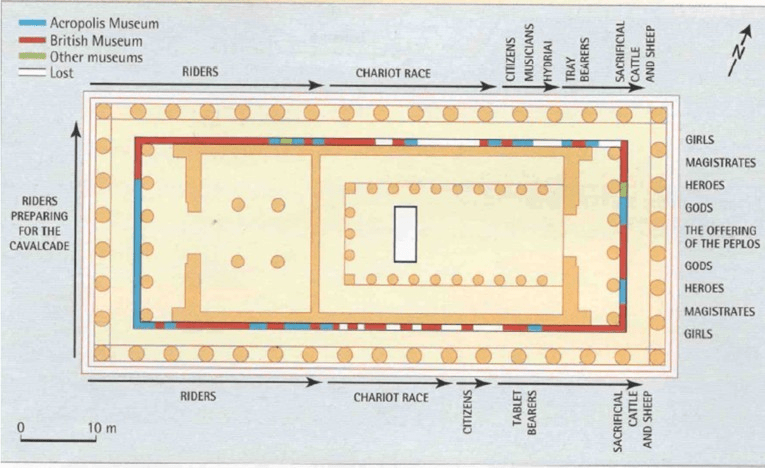
- Frieze – A horizontal sculpted band decorating walls, often showing religious, cultural, or historical scenes.
- Panathenaia – A major festival every four years in Athens to honor Athena, including processions and sacrifices.
- Entasis – Slight curvature in columns to correct optical illusions and improve visual balance.
- Stylobate – The platform or base on which a temple’s columns stand, sometimes slightly raised in the center.
- High and Low Relief – Sculpting techniques where figures are carved to stand out strongly (high) or slightly (low) from the background.
- Phidias – Ancient Greek sculptor and artist who created the statue of Athena and oversaw frieze carvings.
- Elgin Marbles – Sculptures taken from the Parthenon by Lord Elgin, now mostly in the British Museum.
- Cultural Heritage – Important historical, artistic, or religious artifacts representing a country’s culture and identity.
- Ottoman Empire – Empire that ruled Greece from the mid-15th century to the early 19th century.
- Philhellenism – European admiration for Greek culture, art, and history, often inspiring preservation or collection of artifacts.
- Cultural Restitution – The effort to return cultural artifacts taken during colonial or imperial times to their countries of origin.