I. The ecological footprint — a global impact with national differences
II. Who bears the responsibility? People, governments, and corporations
III. Solutions for a more sustainable future
Main question
ecological footprint : making a poster.
Use an A3 sheet to create a poster as if you were the UN. Choose one of two themes: ecological footprint (CO2 consumption) or water resources. Follow these instructions:
- Your poster must be in English.
- Create a strong slogan that captures attention and conveys your message.
- Include a section with subtle and precise information to educate the reader.
- Choose a specific and precise topic within your theme. The more focused your topic is, the better.
- The poster should convince a teenager your age and involve the viewer emotionally or practically.
- Your poster will be judged by another class, and the two best posters chosen by the other class will earn a 10/10.
Documents
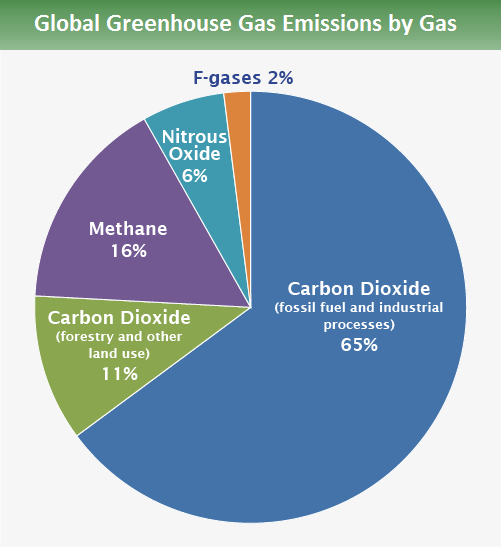
Nitrous Oxide : Agricultural activities, such as fertilizer use, are the primary source of N2O emissions. Fossil fuel combustion also generates N2O.

Word box
- Ecological Footprint – Measures how much land, water, and resources a person or country uses compared to what Earth can provide.
- Carbon Emissions (CO₂ emissions) – The release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere from human activities like burning fossil fuels.
- Climate Change – Long-term changes in Earth’s weather patterns caused mainly by human activities.
- Global Hectare – A unit measuring how much productive land and water area is needed to support one person’s lifestyle.
- Renewable Energy – Energy from sources that can naturally replenish, like solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal.
- Fossil Fuels – Non-renewable energy sources like coal, oil, and natural gas that release greenhouse gases when used.
- Deforestation – The clearing of forests for agriculture, logging, or other human uses, often harming ecosystems.
- Biodiversity Loss – The decrease in the number of species in an ecosystem, reducing its health and resilience.
- Sustainable Agriculture – Farming methods that protect soil, save water, and reduce environmental impact, like crop rotation or agroforestry.
- Energy Efficiency – Using less energy to perform the same task, reducing emissions and costs.
- Carbon-Negative – Removing more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere than is emitted.
- Urban Green Spaces – Parks or green areas in cities that improve air quality, reduce heat, and absorb rainwater.
- Climate Vulnerability – The degree to which a country or community is affected by climate change impacts, regardless of its emissions.
- Corporate Responsibility – How companies’ actions impact the environment, such as through resource extraction or industrial practices.
- Sustainable Urban Planning – Designing cities to reduce energy use, encourage green transport, and improve environmental quality.